Magnetism
What is magnetism?
Magnetism is one of the phenomena by which
materials exert an attractive or repulsive force on other materials.
What causes magnetism in material?
It is the unpaired electrons in the electron
orbit cause magnetism
Examples of paired and unpaired electron
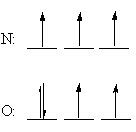 N
is unpaired
N
is unpaired
O
is paired (one of them)
How do you know which electron orbital is paired or un-paired?
Electrons fall into electron shell according to
Hund¡¦s rule. Remember SPDF?? (Chem 11)
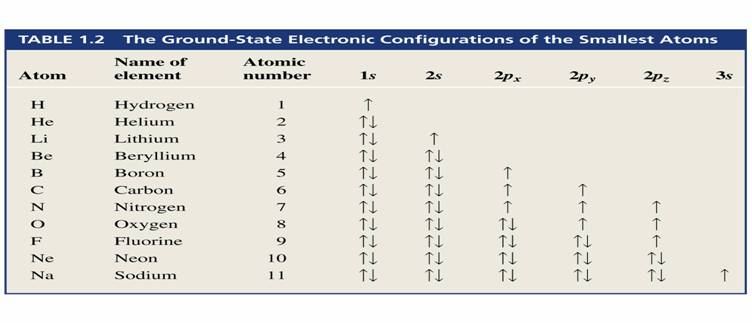
 Example
Example

1S1 2S2 2P3
Right Wrong Wrong
There are four types of
magnetism
1.Ferromagnetic
2.Paramagnetic
3.Diamagnetic
4.Ferrimagnetic (Not going to cover)
-Ferrimagnetic is
too hard to understand at a high school level
Measurements of magnetism
Magnetism is Measure in Magnetic Susceptibility
 The more susceptibility of a material has,
the more magnetic property it processes
The more susceptibility of a material has,
the more magnetic property it processes
Magnetic Susceptibility is to measure the
magnetic property of a material
Q: What is the differences between some of the
materials in the chart above
A: They split off into three groups:
#1
negative value with small Magnetic Susceptibility
#2
positive value with small Magnetic Susceptibility
#3
positive value with relatively big Magnetic Susceptibility compare to above #1
and #2
#4
Zero Magnetic Susceptibility for Vacuum because vacuum does not contain any
material
Ferromagnetic
Any material that possess magnetization WITHOUT an
external magnetic field (current running through a solenoid) is ferromagnetic.
They have large and positive susceptibility. Iron and Cobalt are both examples
of ferromagnetic materials. They do not need an external field because these
materials produce their own magnetic field. Some ferromagnetic materials do not
produce their own magnetic field because the domains inside the material do not
align with each other, and this will be explain shortly.

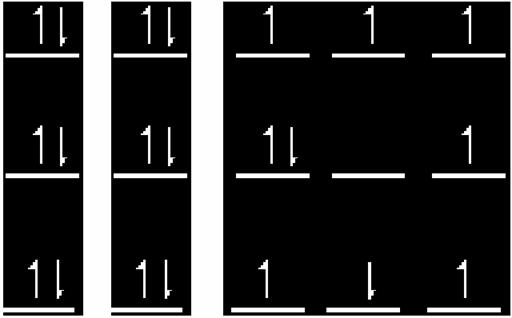
Why are some Ferromagnetic doesn¡¦t attract one another?
If the domains of the material do not align with
each other like the diagram below left (a), they are unmagnetized material. The
magnetic field inside the material cancels out with one another.

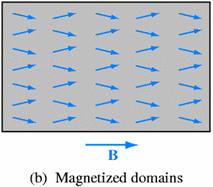
If the domains of the material do align with
each other like the diagram above right (b), they are magnetized material. The
magnetic field inside the material will not cancel out with one another.
Paramagnetic
Any materials that possess magnetization (i.e. attraction
with other magnetized material) WITH an external magnetic field are
paramagnetic. They have small and positive magnetic susceptibility. Aluminum
and Platinum are examples of paramagnetic materials


Platinum Pt
Diamagnetic
Any materials that have very weak and negative
susceptibility to magnetic fields are diamagnetic. Human (mostly), Copper and
Gold are examples of diamagnetic materials.

Gold
Facts
l
Negative magnetic
susceptibility = repel against magnetic fields (diamagnetism)
l
Positive susceptibility =
attract to magnetic fields (para + ferromagnetism)