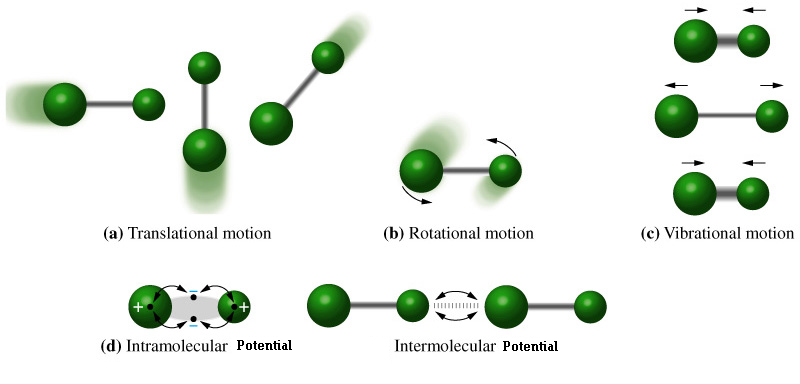
![]() Rotational
Motion – Another form of Kinetic energy in classical mechanics
1/2Iw2 (I = Moment of Inertia, w = Angular velocity)
Rotational
Motion – Another form of Kinetic energy in classical mechanics
1/2Iw2 (I = Moment of Inertia, w = Angular velocity)
![]() Vibration
Motion – Bonds inside a molecule act like small springs with a
potential energy of 1/2kx2 (k = Spring Constant , x =
Displacement)
Vibration
Motion – Bonds inside a molecule act like small springs with a
potential energy of 1/2kx2 (k = Spring Constant , x =
Displacement)
![]() Intramolecular
Potential Energy - Atoms tend to be ionized (have a distinct charge
associated with them) this can cause a magnetic potential energy
between atoms in a molecule.
Intramolecular
Potential Energy - Atoms tend to be ionized (have a distinct charge
associated with them) this can cause a magnetic potential energy
between atoms in a molecule.
![]() Intermolecular
Potential Energy – Molecules themselves can be polar, a good
example of this is water with a negatively charged oxygen and two
slightly positively charged hydrogen atoms. The net charge on a
water molecule in zero but the molecule itself is polar having a
negative and a positive end. Thus polar molecules can have a certain
magnetic potential energy associated with them.
Intermolecular
Potential Energy – Molecules themselves can be polar, a good
example of this is water with a negatively charged oxygen and two
slightly positively charged hydrogen atoms. The net charge on a
water molecule in zero but the molecule itself is polar having a
negative and a positive end. Thus polar molecules can have a certain
magnetic potential energy associated with them.