Methods of Heat Transfer
There are three ways in which energy can be transfer as heat, conduction, convection and radiation.
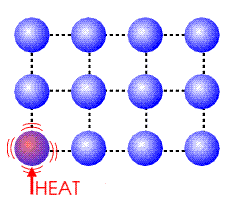
Conduction
Conduction is the transfer of heat through molecular collisions. Fast moving particles can bang into slower moving particles and transfer energy via classical mechanics. Recall that a fast moving particle doesn't imply the object is visibly moving, rather the particle is moving not the material whole.

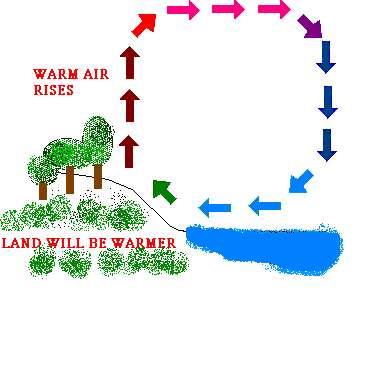
Convection
Convection describes the bulk motion of a gas driven by the property that warm air tends to expand. The expanding gas then takes up more space and its density decreases, if the gas is in a gravitational field then the lighter gas will rise as a more dense gas pushes through it. In this way the heat is carried away.
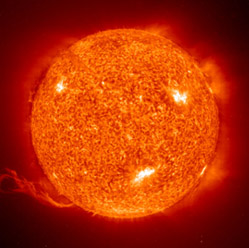
Radiation
Radiation describes the emission of electromagnetic waves including visible light. When an object is heated to a high temperature it is easy to see it visibly glow. This glowing is electromagnetic waves that carry energy away from the system. The color that the system glows is dependent on the energy of the waves (E = hν, E = energy , h = Plank's Constant, ν = Frequency).