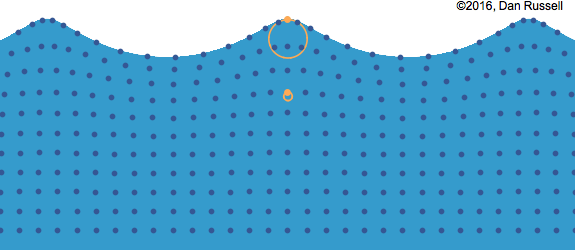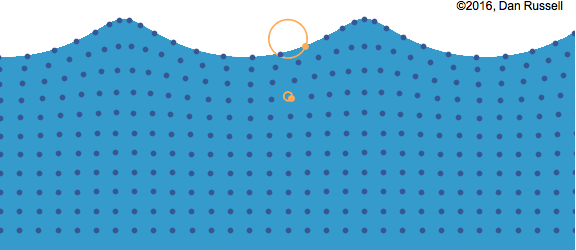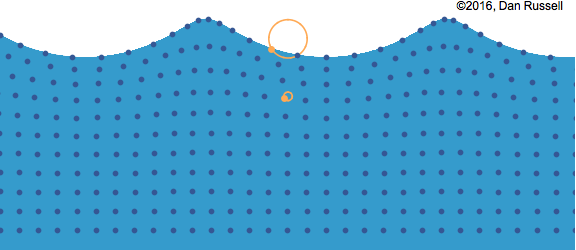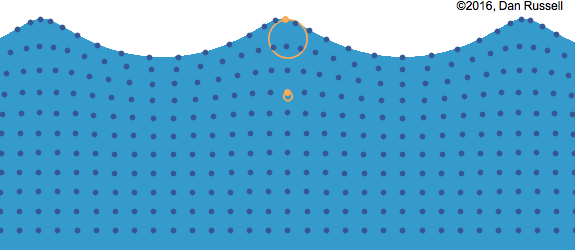
Water wave with particle movement
What is wave?
Wave is a disturbance that carries energy from one location from another while traveling through a medium with some exceptions.
It is often caused by some kind of vibration.
Wave Have Following Properties.
Amplitude: the strength of the wave
Wavelength: distance in which wave shape repeats
Frequency: number of wavelength per unit time
Period: the time it takes for one wave to occur
Wave Velocity: how fast wave travels through

In mechanical waves, there are two ways a vibration could occur. If the particles move perpendicular to the direction of
the energy travel it is called a
transverse wave. If the particles move parallel to the direction of the energy travel it is called a longitudinal wave.
Principle of Superposition
Relation between Formation of Standing Wave and the Chladni Plate
The frequencies where the standing wave occurs are known as natural frequencies of the material that is vibrating.
The set of all possible natural frequencies are called the harmonics of the system.
The natrual frequencies may vary depending on the properties of the material such as the density. The condition where the natural frequencies
occur is called Resonance. When the material is in resonance it experiences a dramatic increase in the amplitude of the vibration.
Interference
Two or more waves can pass through the same medium at the same time without affecting the characteristics of each waves. Only the particles
of the medium are momentarily affected. This is called the interference of the wave and is the special property of the waves.
There are two types of interference.
When two or more waves cross at a point, the displacement at that point is equal to the sum of the displacement of the individual waves.
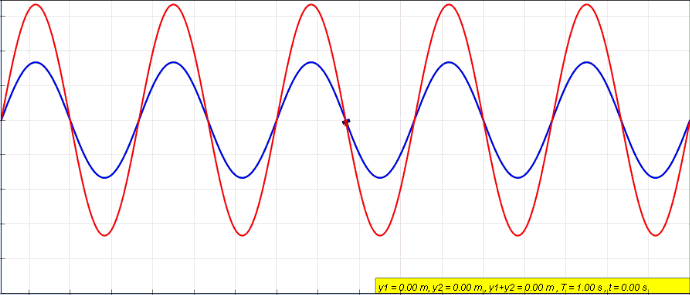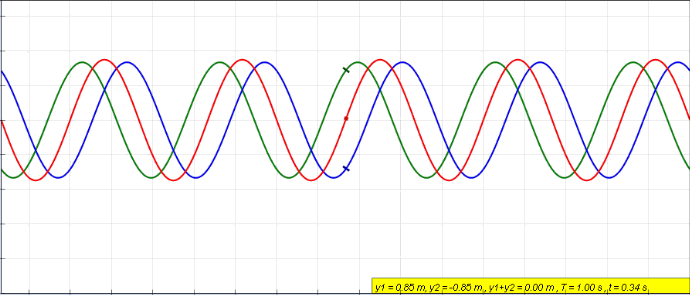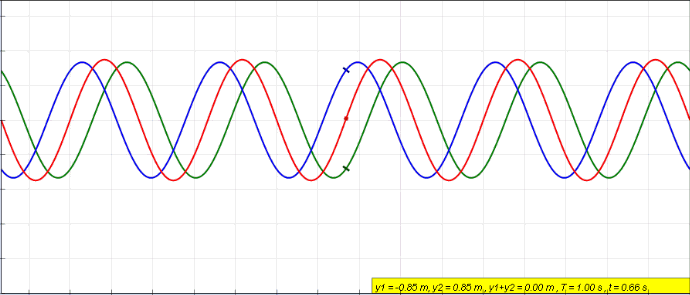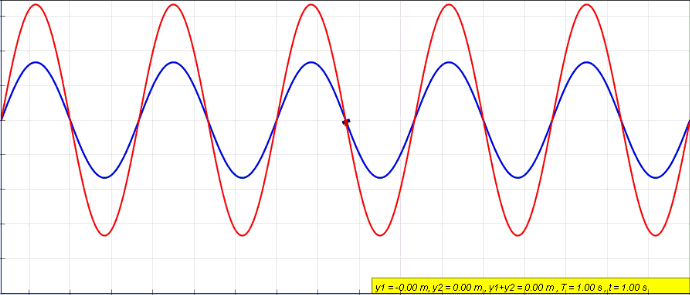
Demonstration of interference and superposition
For the demonstration of the Chladni Plate, a violin bow is stroked at the edge of the plate. As the bow stroked, the string
of the bow will create a vibration that will be transferred to the plate and the vibration will travel through. As the vibration travels through the
plate and reaches the other end, two things happen. First is that some of the energy is tranferred to the new medium, in this case, the air in the form of
screeching sound.
The second is that some of the energy gets reflected back toward the direction where the sound came from. With the reflected energy acting
as a second wave, by the principle of superposition new wave is formed. If you are able to stroke the bow consistently at certain frequencies a wave
that seems like it is not moving toward in any direction, called a Standing Wave is formed. A standing wave have two parts: nodes, where
the particle do not move as the wave is in motion, and anti-node where the particle experience the movement.
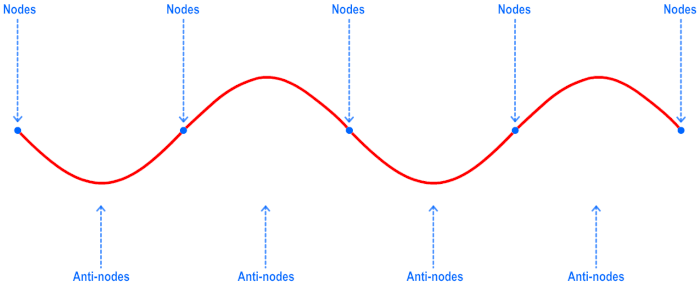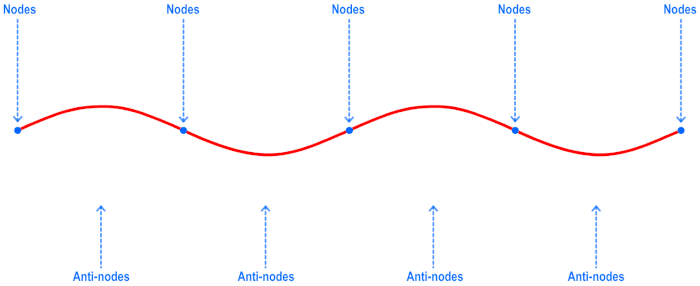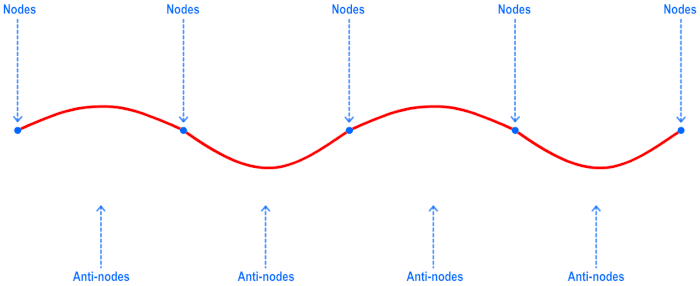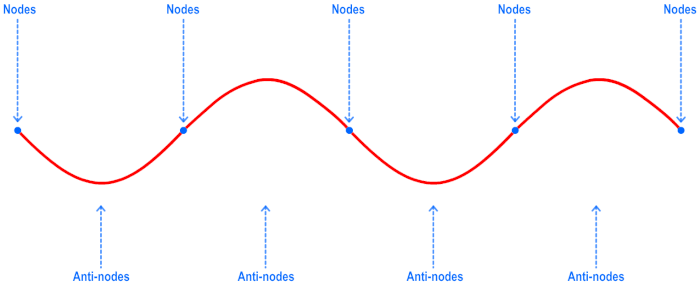
Node & Antinode
How Does Chladni Plate Work?
For the demonstration of the Chladni Plate, a violin bow is stroked at the edge of the plate causing vibration to travel through.
When the plate reaches the end of the plate, so energy will be transferred into the air as a form of the sound wave while the remaining energy gets reflected.
This causes waves to interfere. As a certain level of energy is sent by the bow, the interfering waves will cause resonance to occur through the plate.
This creates a nodal-line and anti-node area where the sand that has been spread on the plate will get pushed away from the anti-node to nodes
and will create a pattern on the plate, letting you see the vibration throughout the entire plate.
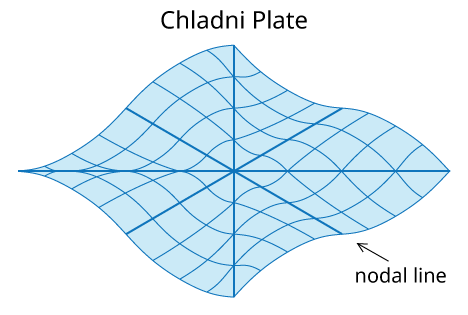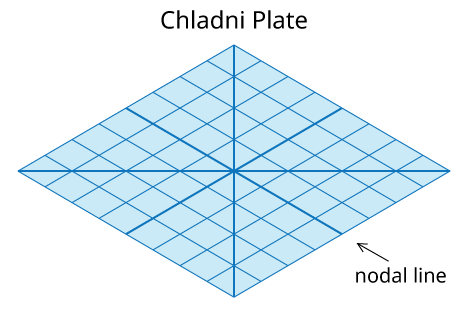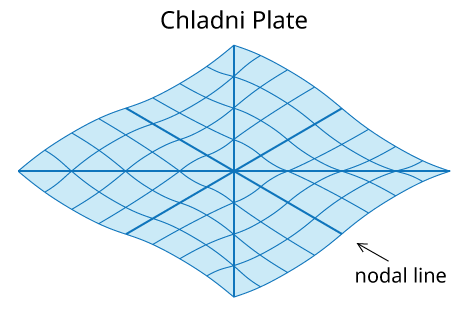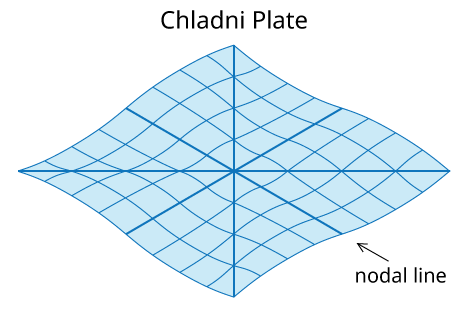
Animation of plate in vibration